What is Leukemia and What Are Its Symptoms? | Prevention and Diagnosis Methods
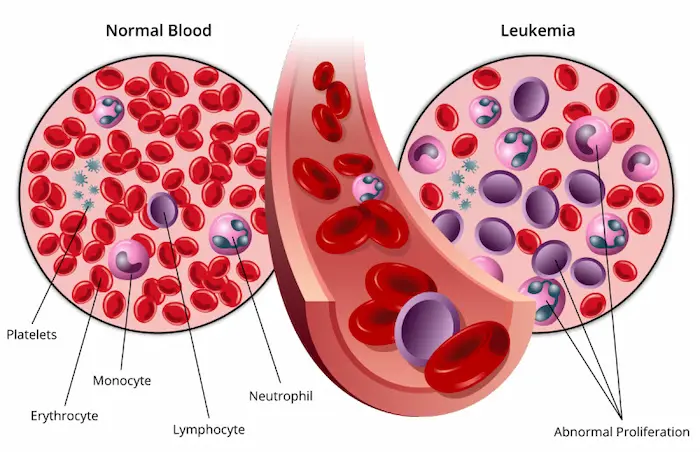
Leukemia is one of the complex and life-threatening diseases that may not show any obvious symptoms in its early stages but gradually affects a person’s health. This disorder occurs when blood cells are produced uncontrollably and abnormally in the bone marrow, interfering with the natural process of blood cell production and the proper functioning of the immune system.
What is Leukemia?
Leukemia is a complex disorder that affects the production and function of blood cells. This disease primarily originates in the bone marrow, a soft and spongy tissue in the center of bones. The bone marrow serves as the source of stem cell production, generating red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Healthy blood cells perform essential functions such as oxygen transport, fighting infections, and aiding in blood clotting. However, in leukemia, the disruption in the production of these cells leads to abnormal cells replacing healthy ones, causing severe health complications.
Types of Blood Cancer
Blood cancer is categorized into three main types, each with different subgroups:
-
Leukemia: This type of blood cancer is more commonly found in children and adolescents and includes various forms such as:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
-
Lymphoma: A type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system and can also impact the bone marrow. Lymphomas are classified into:
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
-
Myeloma: This type of cancer originates in the bone marrow and damages plasma cells. The most common form is Multiple Myeloma, where more than half of the diagnosed patients survive for over five years after detection.
Symptoms of Blood Cancer
The symptoms of blood cancer can vary depending on the type of disease, but some common signs include:
- Extreme Fatigue: Severe weakness and exhaustion that make daily activities difficult.
- Persistent Fever: A prolonged fever, which may indicate the body’s response to infection or abnormal cells.
- Severe Night Sweats: Unusual sweating during the night, leading to soaked clothing and disrupted sleep.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing around 4.5 kg (10 lbs) within 6 to 12 months without any clear reason.
- Frequent Infections: Recurrent infections due to a weakened immune system.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes or Enlarged Liver/Spleen: These symptoms may indicate leukemia or lymphoma.
- Bone Pain: Sensitivity and pain in bones, especially common in leukemia and myeloma.
- Unusual Bleeding or Bruising: Persistent bleeding or bruises that do not heal within two weeks.
These symptoms may resemble other medical conditions, but if they persist for several weeks, consulting a doctor is essential.
Causes of Blood Cancer
Blood cancer occurs when the DNA of blood cells undergoes mutations or genetic changes. These alterations cause the cells to grow abnormally fast or survive longer than usual. As a result, abnormal cells replace healthy ones and occupy space in the bone marrow. This disruption reduces the production of normal blood cells, leading to impaired oxygen transport, weakened infection-fighting ability, and poor blood clotting.
Here’s how genetic changes affect different types of blood cancer:
- Leukemia: DNA mutations, particularly in genes that regulate cell growth and tumor suppression, can be influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Radiation exposure and certain chemicals may trigger these changes.
- Lymphoma: In this type of cancer, genetic changes in white blood cells (lymphocytes) cause uncontrolled proliferation and prolonged survival of abnormal cells. Factors like infections and a weakened immune system may contribute to these mutations.
- Myeloma: In myeloma, plasma cells in the bone marrow multiply abnormally due to new genetic instructions from altered DNA.
For more information: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Cancers
Methods for Diagnosing Blood Cancer
To diagnose blood cancer, a doctor starts by asking about symptoms and medical history, followed by a thorough physical examination. Additionally, various tests and imaging scans may be recommended depending on the suspected type of blood cancer. Some of these diagnostic methods include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the number and levels of blood cells. If leukemia is suspected, the doctor examines the increase or decrease in white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
- Blood Chemistry Test: Measures the levels of chemicals and compounds in the blood. Additional specialized tests may be conducted for a more detailed cancer analysis.
- CT Scan: Produces 3D images of tissues and bones. If myeloma is suspected, a CT scan is used to check for possible bone damage.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Useful for assessing complications in the spine due to leukemia or lymphoma.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scan): A functional imaging technique that detects abnormal activity in tissues and organs. PET scans can be helpful in diagnosing multiple myeloma.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: A sample of bone marrow is extracted and examined to determine the presence of abnormal blood cells and genetic mutations that may cause cancer.
- Blood Cell Examination: A doctor analyzes a blood sample under a microscope to identify abnormal cell appearances. A peripheral blood smear may be ordered to diagnose leukemia or lymphoma.
For more information: Best Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Clinics in Gorgan
Can Blood Cancer Patients Live More Than 5 Years?
Yes, many blood cancer patients can live beyond five years, especially with advancements in early diagnosis and treatment. Survival rates depend on factors such as the type of blood cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their response to treatment.
Blood Cancer Treatment Methods in Gorgan
In Gorgan, various treatment options are available based on the patient’s condition. The choice of treatment depends on the type of blood cancer, patient age, overall health, and potential side effects. Some common treatment methods include:
- Chemotherapy: A primary treatment for blood cancer, chemotherapy in Gorgan utilizes specialized drugs to destroy abnormal blood cells and slow disease progression.
- Radiotherapy: Effective for leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma, radiotherapy in Gorgan uses radiation to damage cancerous cell DNA and halt their growth.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment strengthens the immune system to fight cancer and is sometimes combined with other therapies for better results.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genetic mutations that cause healthy cells to become abnormal.
- CAR T-Cell Therapy: A new treatment modifying T cells to fight cancer more effectively, used for certain types of leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Gorgan.
- Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Advanced treatment options available in Gorgan for patients requiring intensive therapy. Stem cell transplants help restore damaged bone marrow following chemotherapy or radiation.
Patients in Gorgan can access advanced cancer treatment options, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Various medical centers, such as Shafa Radiotherapy Oncology Center, provide specialized services with modern equipment and expert teams for blood cancer treatment.
Prevention of Blood Cancer
Although the exact cause of blood cancer is not fully understood, researchers have identified several factors that may increase the risk of developing this disease. Due to its complexity, complete prevention is not possible, but taking certain precautions can help reduce the risk.
Risk Factors for Blood Cancer
- Exposure to Radiation: Prolonged exposure to radiation sources can damage DNA and lead to genetic mutations that may result in blood cancer.
- Contact with Harmful Chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as benzene and pesticides, have been linked to an increased risk of blood cancer.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a compromised immune system who are more prone to infections may have a higher risk of developing blood cancer.
- Family History: A history of blood cancer in the family can increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Genetic Disorders: Some inherited conditions, such as Down syndrome or post-chemotherapy syndromes, can raise the risk of blood cancer.
Ways to Reduce the Risk of Blood Cancer
To lower the chances of developing blood cancer, consider the following preventive measures:
- Minimize exposure to radiation and harmful chemicals.
- Strengthen the immune system through a healthy lifestyle.
- Undergo regular medical check-ups, especially if you have a family history of blood cancer.
Conclusion
Blood cancer is a complex and challenging disease that requires early diagnosis and specialized treatment. Although complete prevention is not possible, awareness of risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the chances of developing this condition.
Additionally, regular health monitoring and consulting a doctor in case of suspicious symptoms can play a crucial role in early detection and effective treatment. Advances in blood cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapies, have significantly improved patients’ quality of life and survival rates. Prioritizing health and routine medical evaluations, especially for those with a family history of blood cancer, can be an essential step toward timely prevention and treatment.

No comment