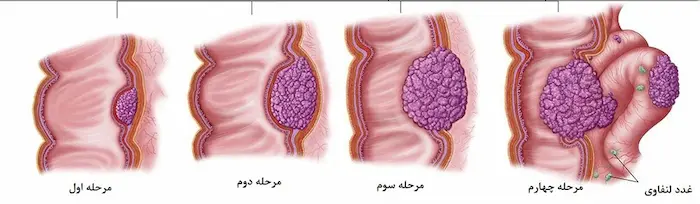
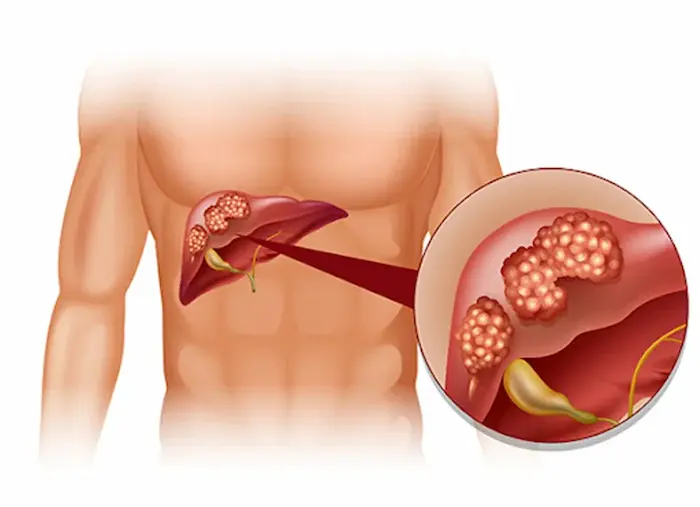
Cancer and How It Forms
Under normal conditions, the cells of the body divide in a regulated and controlled manner. These divisions typically occur to replace dead cells or repair damaged tissues. However, in cancer, this controlled process is disrupted. Due to genetic mutations, cancer cells lose the ability to regulate their division and grow uncontrollably. These cells cluster together to form tumors, which can exert pressure on surrounding tissues and cause damage.
Metastasis and Cancer Spread
Metastasis refers to the process in which cancer cells detach from their original site and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. This spread can affect various organs such as the liver, lungs, bones, and brain, leading to the formation of new tumors in these areas. Interestingly, when cancer spreads to another part of the body, the new tumor remains the same type as the original cancer. For example, if breast cancer metastasizes to the bones, the new tumor is still considered breast cancer rather than bone cancer.
Ways Cancer Cells Spread
Cancer cells can spread in the body through three main pathways:
- Through the Circulatory System: Cancer cells may enter the blood vessels and travel to other parts of the body.
- Through the Lymphatic System: The lymphatic system, which includes lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels, plays a significant role in transporting cancer cells to other organs.
- Local Invasion: Cancer cells may directly invade and spread into the surrounding tissues.
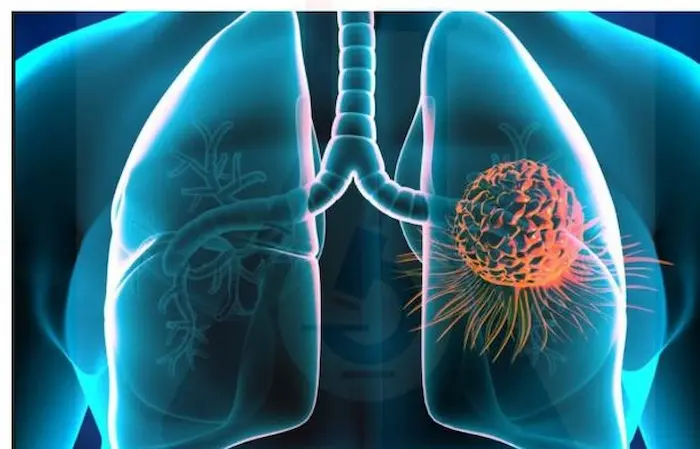
Why Is Metastasis Dangerous?
Metastasis is one of the leading causes of death in cancer patients. When cancer cells detach from their original site and spread to other parts of the body, treatment becomes significantly more challenging. At this stage, the disease affects the entire body, making early detection and prompt treatment crucial. Metastasis typically occurs in advanced stages of cancer, which is why available treatments may not always yield effective results.
Diagnosis and Symptoms of Metastasis
Before cancer reaches the metastatic stage, certain early symptoms may appear in the body. These symptoms can include:
- Wheezing or shortness of breath: Commonly seen in lung cancer.
- Fever or infections: Frequently associated with brain and bone cancers.
- Difficulty swallowing: Observed in throat and lung cancers.
- Weakness and fatigue: A general symptom present in many types of cancer.
- Lumps in the neck, underarms, or groin: These may indicate the spread of cancer to the lymph nodes.
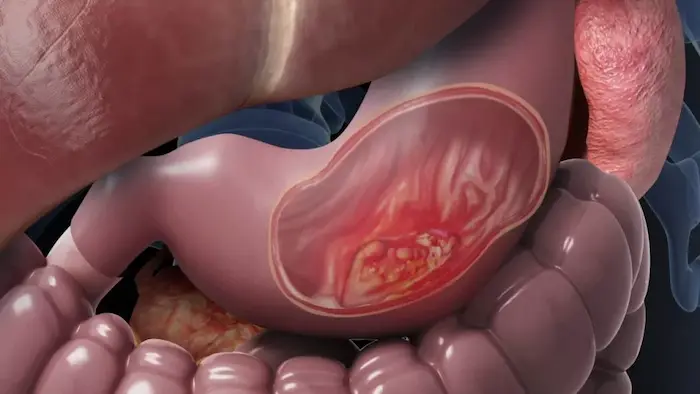
Physical Changes Caused by Cancer
Sometimes, cancer does not spread rapidly throughout the body but instead causes noticeable physical changes that can aid in its diagnosis. Some of these changes include:
- Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool: Often observed in colorectal cancer.
- New lumps in the body: Such as lumps in the neck or underarms.
In previous articles, we discussed 13 warning signs of cancer that should not be ignored. These symptoms may indicate the presence of cancer in the body, and paying attention to them can assist in early diagnosis.
Cancer Prevention and Treatment
Preventing cancer and stopping its spread to other parts of the body is crucial. Some effective prevention methods include quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, protecting the skin from UV radiation, and maintaining a healthy diet. If cancer is detected in its early stages, various treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies can help stop its progression.
Final Words
The spread of cancer within the body remains one of the biggest challenges in its treatment. Being aware of early symptoms and bodily changes can aid in early detection and help prevent the progression of cancer. Additionally, following preventive measures and seeking timely medical attention play a crucial role in controlling and treating cancer effectively.


No comment