What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer is a serious disease that occurs due to the abnormal growth of cells in the liver tissue. The liver, the largest internal organ in the body, performs vital functions such as producing bile, storing nutrients, metabolizing fats, and detoxifying the blood. This organ is composed of blood vessels and bile ducts that transport bile from the liver to the gallbladder or digestive system. Additionally, the liver plays a crucial role in producing clotting factors and removing toxins from the body.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the number of liver cancer cases is on the rise. In 2021 alone, more than 42,000 people were expected to be diagnosed with this disease. Liver cancer is more common in older individuals, particularly those over 55 years of age. Cirrhosis, which can result from excessive alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, is one of the factors that increases the risk of liver cancer.
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer occurs when liver cells start to grow abnormally and rapidly, forming a tumor. These tumors can be either malignant (cancerous) or benign (non-cancerous). When these cancerous cells originate in the liver, they are called primary liver cancer. One of the most common types of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), where liver cells become undifferentiated and transform into cancerous cells.
Many individuals with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not show symptoms until the disease has reached advanced stages. As a result, this type of cancer is often difficult to detect in its early stages.
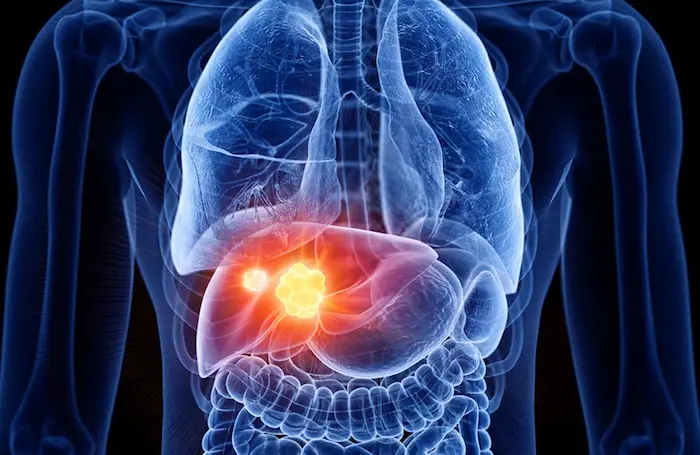
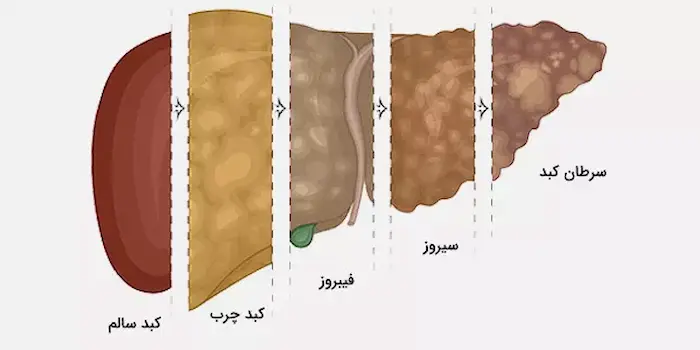
Causes of Liver Cancer (Factors that Increase the Risk)
Although the exact cause of liver cancer is not fully understood, many cases of this disease are linked to liver damage and the formation of scar tissue in the liver, known as cirrhosis. The most common causes of liver cancer include chronic hepatitis B and C infections. Studies have shown that preventing hepatitis can significantly reduce the risk of liver cancer.
-
Age
This disease is more common in older individuals. In the United States, the average age of onset is 63. As people age, liver damage caused by various diseases like hepatitis or cirrhosis increases, which can raise the risk of liver cancer. -
Gender
Men are more likely to develop liver cancer than women. The reasons for this difference may include hormonal differences, riskier behaviors like higher alcohol consumption and smoking among men, as well as biological differences in how the body processes toxins. -
Race and Ethnicity
In the United States, Asian and Pacific Islander populations are at a higher risk of liver cancer. This is primarily due to the higher prevalence of hepatitis B and C infections in these groups. Additionally, some research suggests that genetic and cultural factors may also contribute to the increased risk. -
Obesity and Overweight
Obesity and being overweight indirectly increase the risk of liver cancer. This condition can lead to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a liver disease seen in obese individuals, which can progress to cirrhosis and eventually liver cancer. The accumulation of fat in the liver causes inflammation and damage to liver cells, leading to scarring and cirrhosis. -
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Chronic heavy drinking can lead to cirrhosis of the liver. Cirrhosis is one of the most significant risk factors for liver cancer. Alcohol directly damages liver cells, leading to tissue destruction and scarring. This damage can create the environment for the abnormal proliferation of liver cells, ultimately resulting in cancer. -
Smoking
Tobacco use is another risk factor for liver cancer. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can damage the liver and exacerbate liver damage. Additionally, smoking increases the likelihood of heart disease and cirrhosis. -
Anabolic Steroids
Long-term use of anabolic steroids (male hormones) to enhance muscle mass can lead to an increased risk of liver cancer. These steroids may damage the liver and alter its structure and function. However, steroids like hydrocortisone and prednisone, used as anti-inflammatory medications, do not carry the same risk. -
Arsenic
Chronic exposure to natural arsenic (often through contaminated drinking water) can increase the risk of liver cancer. In certain parts of the world, particularly in rural and underdeveloped areas, arsenic is a contaminant in drinking water sources, which may contribute to liver diseases and cancer. -
Aflatoxins
Aflatoxins are carcinogenic substances produced by fungi that are commonly found in foods such as wheat, corn, rice, soybeans, and nuts. These fungi thrive in warm and humid environmental conditions, and long-term exposure to aflatoxins is a significant risk factor for liver cancer, especially in individuals infected with hepatitis B or C. -
Exposure to Chemicals
Chemicals such as vinyl chloride (used in making certain plastics) and thorium dioxide (formerly used in X-ray imaging) may increase the risk of liver cancer. These substances can damage the liver and promote tumor growth. However, strict regulations to limit exposure to these chemicals have been enforced in many countries in recent years. -
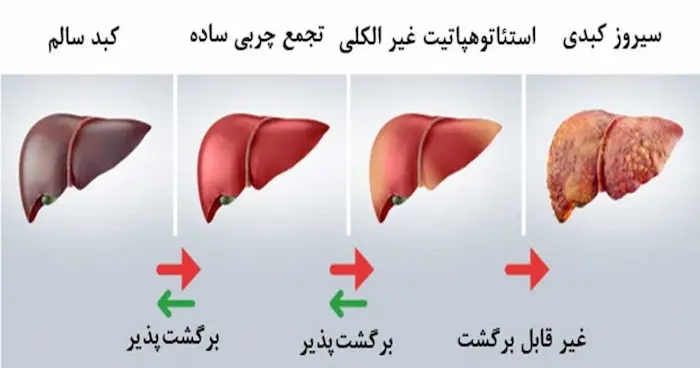
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis occurs when liver cells are damaged and replaced with scar tissue. This condition is primarily caused by complications from diseases like chronic hepatitis or prolonged alcohol use. Cirrhosis reduces liver function, and liver cells gradually transform, making it easier for them to become cancerous. People with cirrhosis are at high risk for liver cancer. -
Hereditary Metabolic Diseases
Certain rare metabolic disorders, such as hemochromatosis (a condition that causes iron to accumulate in the liver), tyrosinemia (elevated levels of the amino acid tyrosine), and Wilson’s disease (elevated copper in the liver), can lead to liver damage and cirrhosis, increasing the risk of liver cancer. -
Diabetes
Diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, increases the risk of liver cancer. People with diabetes may be at risk for conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which can progress to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Additionally, diabetes can contribute to cancer development by increasing insulin resistance and inflammation in the liver.
Read More: Does Stress Cause Cancer? Scientific Examination of the Link Between Psychological Stress and Cancer.
Methods of Diagnosing Liver Cancer
There are various methods to diagnose liver cancer, which help doctors get an accurate understanding of the patient’s liver condition. These methods include imaging, blood tests, and liver tissue biopsy.
Liver Ultrasound
Ultrasound is one of the most common methods for diagnosing this disease. It is non-invasive and quick, typically used as the first method for diagnosing liver cancer. Using sound waves, ultrasound creates images of the liver and can identify tumors or abnormal changes in the liver. The accuracy of this method depends on the experience and skill of the person performing it.
AFP Test (Alpha-Fetoprotein)
This test measures the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood. This protein is typically produced in liver cancers and other types of cancers. A high AFP level in the blood may indicate liver cancer, although an increase in AFP can also occur due to other reasons.
CT Scan of the Liver
A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to create detailed, cross-sectional images of the liver. This method is more accurate than ultrasound and is usually used to assess the size and location of liver tumors.
Liver Angiography
In this method, a contrast material is injected into the liver through a vein to provide detailed images of blood vessels and liver tumors. This method is particularly useful for identifying small tumors and blood vessels that may supply blood to the tumors.
Liver Biopsy
In a liver biopsy, a sample of liver tissue is taken and examined under a microscope. This method helps diagnose the type of cancer and determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant, offering precise information about liver cancer.
Read More: 13 Warning Signs of Cancer You Should Never Ignore
Types of Liver Cancer Treatments
The treatment for liver cancer depends on the type and stage of cancer and may involve a combination of various methods. Below are some common treatments for liver cancer:
Drug Therapy
This method involves using medications aimed at stopping the growth and multiplication of cancer cells. There are various drugs available for treating liver cancer, and doctors will prescribe appropriate medications based on the severity of the disease and the type of tumor.
Surgery
If the tumor is removable, surgery is considered the best treatment option. In liver cancer surgery, the affected part of the liver is removed. This method is usually effective for small tumors that are limited to one part of the liver.
Alcohol Injection
In this method, pure alcohol is injected into cancerous tumors to dry out and kill the cancer cells. This method is used for smaller cancers and in cases where surgery is not possible.
Radiofrequency Ablation
This method uses radioelectric currents to destroy cancer cells. Thin needles are inserted through the skin into the tumor, and they are heated with electric currents to destroy the cancer cells.
Chemoembolization
In this method, strong chemotherapy drugs are directly injected into the liver. This method is typically used for patients with cancer limited to one part of the liver who need intense chemotherapy.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy uses cold temperatures to destroy cancer cells. This method is useful for small tumors and when surgery is not feasible.
Radiotherapy
This treatment uses high-energy waves to destroy cancer cells. The radiation may come from external devices or from radioactive materials directly sent to the liver to target the tumor.
Liver Cancer Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using specific drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs can be administered intravenously or taken orally, and are generally used when cancer has spread.
Liver Transplant
In some cases, a liver transplant is the only treatment option. In this procedure, the patient’s liver is removed, and a healthy liver from a donor replaces it. This method is usually effective for people with small tumors in the early stage of liver cancer.
Sorafenib (Nexavar)
This drug is specifically used to treat advanced liver cancer. Sorafenib prevents the growth of cancer tumors and helps reduce blood supply to the tumor.
Read More: Comprehensive Introduction to Tomotherapy | The Most Advanced Radiotherapy Method for Cancer Treatment
Methods of Preventing Liver Cancer
Preventing liver cancer plays a key role in reducing the risk of developing the disease. Specifically, the focus is on preventing infections like Hepatitis B and C, which are considered the main causes of liver cancer. Here are some important prevention methods:
-
Preventing Hepatitis B and C Infections
As mentioned, Hepatitis B and C infections are the primary causes of liver cancer. Therefore, preventing these infections is of particular importance. For Hepatitis B, vaccination is the most effective prevention method. While there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, there are effective treatments to manage this condition. -
Vaccination
- Hepatitis B Vaccination: The Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all children in the United States and is also suggested for adults in many countries to prevent infection. If you have not been vaccinated, you can consult with your doctor about receiving the vaccine.
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus) Vaccine: This vaccine helps prevent cancers such as cervical cancer and other cancers. Although it does not have a direct connection to liver cancer, its impact in reducing the risk of other cancers contributes to overall public health.
-
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can reduce the risk of liver diseases and liver cancer. These activities help maintain a healthy weight and strengthen the immune system.
- Fitness and Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Individuals should keep their weight within a healthy range. Obesity increases the risk of liver diseases like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and cirrhosis.
- Limiting Alcohol and Drug Use: Excessive alcohol consumption is a common cause of liver disease and cirrhosis. To reduce the risk of liver cancer, it is important to limit alcohol consumption and avoid drug use.
-
Healthy Diet
- Fruits and Vegetables: Research suggests that some fruits and vegetables, such as grapefruit, blueberries, grapes, and cruciferous vegetables (like cabbage and broccoli), may reduce the risk of liver diseases.
- Liver-Friendly Foods: Fatty fish (such as salmon and tuna), olive oil, nuts, and seeds are also beneficial for liver health.
- Avoiding Fatty Foods: Poor dietary habits are detrimental to health. Consuming fatty and processed foods can lead to liver damage, so it is recommended to avoid such foods.
-
Regular Screenings for At-Risk Individuals
People at high risk of liver cancer (such as those with a family history or who are infected with Hepatitis) should undergo regular liver ultrasounds and blood tests for alpha-fetoprotein. These tests can help detect liver cancer early.
Is Liver Cancer Fatal?
This disease, particularly primary and secondary liver cancers, can be fatal in advanced stages. If the cancer spreads to other parts of the body (secondary cancer), the prognosis becomes more challenging. In some cases, patients may experience bleeding from the esophagus or vomit blood, indicating cancer spread.
Early detection of cancer is the most important factor in increasing the chances of successful treatment. For this reason, individuals at risk should receive regular medical care.
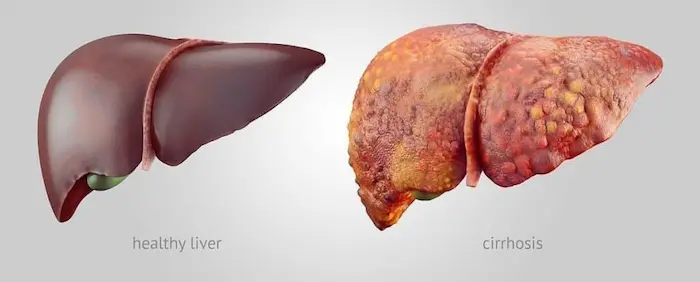
Conclusion
Liver cancer may not show any symptoms in its early stages, which is why it is typically diagnosed at more advanced stages. Since there are no comprehensive screening tests for this cancer, individuals at risk should consult with their doctor to take appropriate preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing this disease.


No comment